HPE 3PAR Volume Management
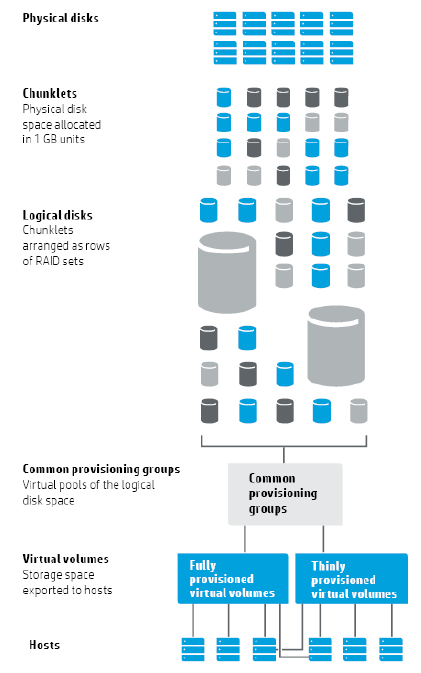
The 3PAR Operating System has a logical volume manager that provides virtual volume abstraction. Part 1 is a quick overview to explain the architecture at a high level and provide a basic introduction to the concepts. [Link to Part 2 when available]
| Chunklets | 1 GB chunklets of physical disks, treated like “mini” disks |
| Logical Disks | chunklets from hundreds of drives form RAID sets |
| Volume Spaces | user, snapshot, and admin spaces striped across logical disk regions |
| Virtual Volumes | base or snapshot, full or thin provisioned, mapped to spaces |
| Virtual LUNs | virtual volumes made visible to hosts as LUNs |
Physical Disks
Every physical disk admitted into the 3PAR system is divided into 1 GB chunklets. A chunklet is the most basic component of data storage in the 3PAR Operating System. Chunklets are blocks of space and form the basis of the RAID sets.
Logical Disks
The logical disk layer is where RAID functionality occurs. A logical disk is a collection of chunklets arranged as stripes of a RAID set. Logical disks will consist of chunklets belonging to the same drive type (NL-SAS, FC, or SSD).
Common Provisioning Group
Common Provisioning Groups (CPG) define the logical disks’ characteristics, including RAID type and disk type for chunklet selection.
Virtual Volumes
Virtual Volumes create the data layer presented to host servers; in traditional terminology, virtual volumes are LUNs.
Leave a Reply